Dental implants are a restorative dental treatment that offers patients a permanent solution for missing teeth. These titanium posts, surgically placed into the jawbone, serve as artificial tooth roots, and they provide a foundation for replacements. Here is more information on these dental devices, the process involved, and the associated benefits for oral health and function:
What Are Dental Implants?
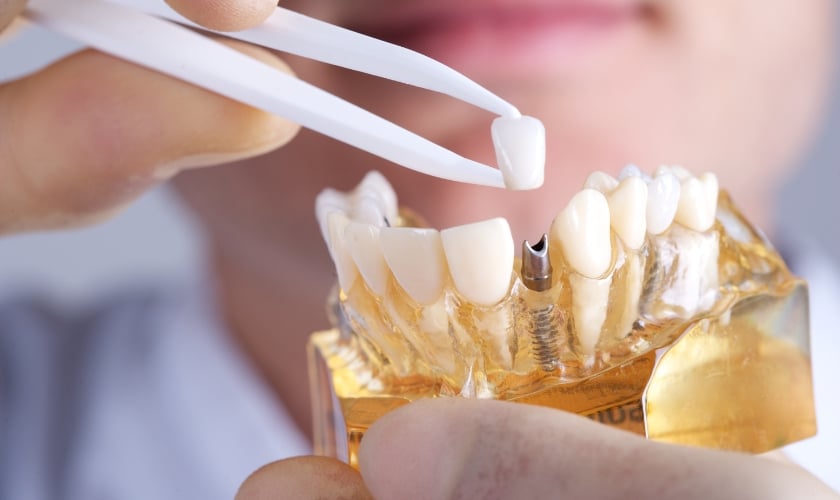
Dental implants are small titanium screws that replace the roots of missing teeth. The implant integrates with the jawbone through a process called osseointegration, creating a strong and permanent foundation. Once the implant has fused with the bone, a crown, bridge, or denture is attached to restore function and appearance.
The titanium material used is biocompatible, meaning the body readily accepts it without rejection. This compatibility allows the implant to bond naturally with the surrounding bone tissue over several months. The result is a stable, durable tooth replacement that can last for decades with proper care.
What Purpose Do They Serve?
Dental implants serve multiple functions beyond simply replacing missing teeth. They maintain the integrity of the jawbone by providing the stimulation that natural tooth roots would provide, thereby preventing the bone loss that commonly occurs after tooth extraction. Without this stimulation, the jawbone can deteriorate, leading to changes in facial appearance and additional oral health complications.
The implants also preserve the alignment of remaining natural teeth. When a tooth is lost, adjacent teeth tend to shift into the space left by the missing tooth, creating alignment issues and bite problems. Dental implants fill these gaps and maintain proper tooth spacing.
What Does the Process Involve?
The process typically begins with a comprehensive examination and treatment planning phase. The dentist will evaluate oral health, take X-rays or CT scans, and determine if a patient has sufficient bone density to support an implant. If bone grafting is necessary, this procedure may be completed before implant placement.
Implants are placed surgically under local anesthesia in the dental office. The dentist creates a small incision in the gum tissue, drills a precise hole in the jawbone where the implant will be placed, and then inserts the titanium post into this space. The healing period following surgery typically lasts 3 to 9 months, during which osseointegration occurs.
Once the implant has integrated with the bone, an abutment is attached to connect the implant to the final restoration. The custom crown, bridge, or denture is then fabricated and secured to the abutment, completing the restoration process. The entire treatment timeline ranges widely, depending on individual healing rates and treatment complexity.
How Is Oral Health Affected?
Dental implants have a positive impact on overall oral health by promoting proper oral hygiene. Implants can be cleaned just like natural teeth with regular brushing and flossing, making it easier to maintain good oral hygiene and prevent plaque buildup around the restoration. When bone loss occurs due to missing teeth, it can affect the stability of surrounding teeth and create pockets where bacteria can accumulate. Dental implants prevent this bone loss and help maintain the natural contours of the gums and facial tissues.
Improve Your Oral Health
Dental implants offer a comprehensive solution for tooth replacement that benefits both oral health and quality of life. The procedure addresses the functional and aesthetic concerns associated with missing teeth while preventing the long-term complications of bone loss and tooth shifting. If you want to learn more about these dental devices, talk to a qualified dental professional.