Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun significantly increases the risk of developing skin cancer. UV radiation damages DNA in skin cells, which can lead to abnormal growth and potentially cancerous changes. Limiting sun exposure and using protective measures helps reduce this risk and supports long-term skin health. Here are a few things to know about the connection between skin cancer and sun exposure:
Skin Risks
UV radiation from the sun is a primary cause of skin cancer because it damages DNA in skin cells over time. Extended outdoor activity, whether for work or recreation, such as swimming or hiking, increases cumulative UV exposure, and tanning beds add concentrated UV radiation that also raises risk. Genetics, family history, and fair skin contribute to susceptibility, while age and immune function influence how the body responds to UV damage.
Older adults tend to show higher rates of skin cancer, though younger people can also develop the condition. Having multiple moles or a history of sunburns can indicate elevated risk, and monitoring skin changes supports early detection. Understanding these factors together provides a clearer view of individual vulnerability and potential prevention needs.
Cancer Types
Dermatologists commonly diagnose three primary types of skin cancer, each with unique growth patterns and treatment factors. Early detection improves outcomes and enables more targeted interventions. Understanding how these cancers behave helps guide monitoring and informs discussions with a dermatologist.
- Basal cell carcinoma: slow-growing, rarely spreads, often appears as a pearly bump or flesh-colored patch, usually found on sun-exposed areas
- Squamous cell carcinoma: can spread if left untreated, may appear as a firm red nodule or scaly patch, and commonly develops on sun-exposed skin.
- Melanoma: the most aggressive type, can spread quickly, often appears as a mole that changes in color, size, or shape, and develops anywhere on the body
Identifying each type early provides the best chance for effective treatment and long-term skin health.
Prevention Strategies
Daily exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun can cause changes in skin cells over time, particularly in areas frequently exposed. Using sunscreen with adequate SPF, wearing protective clothing, and limiting direct sun exposure during peak hours can help manage overall UV exposure. Observing these practices may influence the likelihood of skin changes and long-term skin damage associated with prolonged sun exposure.
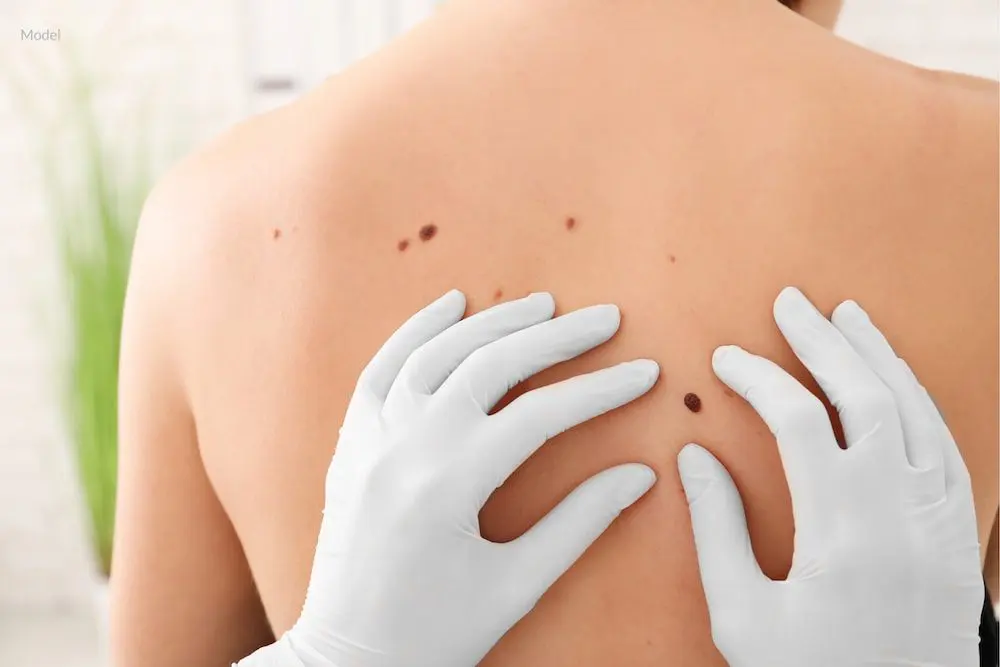
Skin Screenings
Regular skin examinations are recommended for high-risk individuals, as professional screenings can detect changes that might be overlooked. Self-examinations at home complement clinical care, and monthly checks help identify new or evolving spots. Photography can help track changes in moles over time, making monitoring more precise. Any alterations in size, color, or shape should prompt medical evaluation, as early detection improves treatment outcomes.
Taking Action For Skin Cancer
Daily habits help reduce the risk of UV-induced skin damage, and applying sunscreen every morning adds an extra layer of protection. Limiting time in direct sunlight further supports overall skin health. Regular dermatologic screenings can detect early signs of skin cancer, while professionals provide guidance on personalized prevention strategies. Schedule a skin exam to evaluate your risk and discuss protective measures with a qualified dermatologist.